Event Viewer is often the first troubleshooting tool that you will use to diagnose a problem and gather troubleshooting information. Event Viewer has many improvements and new features to help you search for event information on both a local and a remote computer. You can create custom views to save filtered information, subscribe to a remote log to forward events, and view event data for specific Windows applications and services.
Event Viewer can be accessed under the Diagnostics category in Server Manager or by launching it from the command line by typing eventvwr.msc. This opens MMC with the Event Viewer snap-in module loaded. Event Viewer has been categorized into five key areas.
Following are the descriptions of five key areas:
Event Logs Summary: Event Logs Summary aggregates events from key logs. Data is categorized by error, warning, information, and audit success events. You can see a snapshot of events that have occurred over the last hour, 24 hours, and 7 days. You can also view the total number of events, recently accessed nodes, and a summary of log properties.
Windows Logs: The Windows Logs area includes the Application, Security, and System logs. It also includes two new logs, the Setup Log and the ForwardedEvents log. Windows logs store events from earlier applications and events that apply to the entire system.
Applications and Services Logs: Applications and Services Logs have been extended to include new log files for hardware events, Internet Explorer, and key management services, and Windows components. These logs give you a direct approach for gathering troubleshooting and diagnostic information.
Subscriptions: The Subscriptions area gives you the ability to collect copies of events from multiple computers and store them locally. The subscription specifies exactly which events will be collected and in which log they will be stored. Event collecting depends on the Windows Remote Management and the Event Collector services.
Custom Views: The Custom Views lists displays views that you have saved after querying, analyzing, and sorting events. You can use these views for future references. You can select a custom view, apply the underlying filter, and the results are displayed.
Tabs
- About Us (1)
- Asp.Net (8)
- C Sharp (7)
- Contact me (1)
- Earn Online (1)
- General News (1)
- IT News (475)
- Motivational SMS (4)
- SQL (1)
- Tricks and Tips (7)
- Trouble Shooting (13)
- VB.Net (10)
My Blog List
-
What is there in ones name! Here is a LOT!12 years ago
Blog Archive
How To Install or Remove a Font in Windows
To Reinstall the Accepted Fonts Included With Windows
The afterward fonts are included with Windows and are installed on every computer:
• Courier New (TrueType, including Bold, Italic, and Bold Italic variations)
• Arial (TrueType, including Bold, Italic, and Bold Italic variations)
• Times New Roman (TrueType, including Bold, Italic, and Bold Italic variations)
• Symbol (TrueType)
• Wingdings (TrueType)
• MS Serif
• MS Sans Serif
If any of the accepted fonts that are included with Windows are missing, you can run Windows Setup again. Setup replaces missing or afflicted files. If these accepted fonts are missing, added Windows files may aswell be missing, and Setup corrects these problems.
Note On Microsoft Windows NT 4.0, Microsoft Windows 2000, Microsoft Windows XP, and Microsoft Windows Server 2003, you have to be an ambassador to add and abolish fonts.
Adding New Fonts
Windows supports TrueType fonts or fonts that are distinctively advised for Windows, and these fonts are accessible commercially. Some programs aswell cover appropriate fonts that are installed as allotment of the affairs installation. Additionally, printers frequently appear with TrueType or appropriate Windows fonts. Follow the admonition that appear with these articles to install these fonts.
To manually install or re-install a font:
1. Click Start, and again bang Run.
2. Type %windir%fonts, and again bang OK.
3. On the File menu, bang Install New Font.
4. In the Drives box, bang the drive that has the billowing or CD-ROM that contains the fonts you wish to add. If you are installing fonts from a billowing disk, this is about drive A or drive B. If you are installing the fonts from a bunched disc, your CD-ROM drive is about drive D. Double-click the binder that contains the fonts.
5. Click the chantry you wish to add. To baddest added than one chantry at a time, columnist and authority down the CTRL key while you bang anniversary font.
6. Click to baddest the Copy Fonts To Fonts Binder analysis box. The WindowsFonts binder is area the fonts that are included with Windows are stored.
7. Click OK.
Removing Fonts
To absolutely abolish fonts from the harder disk:
1. Click Start, and again bang Run.
2. Type %windir%fonts, and again bang OK.
3. Click the chantry you wish to remove. To baddest added than one chantry at a time, columnist and authority down the CTRL key while you bang anniversary font.
4. On the File menu, bang Delete.
5. When you accept the “Are you abiding you wish to annul these fonts?” prompt, bang Yes.
To anticipate a chantry from loading after removing it from the harder disk, move the chantry from the Fonts binder into addition folder. Use this adjustment for troubleshooting purposes. This action does not absolutely abolish the font, because chantry anthology advice is not deleted. However, it prevents the chantry from loading.
APPLIES TO
• Microsoft Windows Server 2003, Enterprise Edition (32-bit x86)
• Microsoft Windows Server 2003, Datacenter Edition (32-bit x86)
• Microsoft Windows Server 2003, Accepted Edition (32-bit x86)
• Microsoft Windows Server 2003, Web Edition
• Microsoft Windows Server 2003, Enterprise x64 Edition
• Microsoft Windows Server 2003, 64-Bit Datacenter Edition
• Microsoft Windows XP Professional
• Microsoft Windows XP Home Edition
• Microsoft Windows XP Tablet PC Edition
• Microsoft Windows 2000 Advanced Server
• Microsoft Windows 2000 Datacenter Server
• Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional Edition
• Microsoft Windows 2000 Server
• Microsoft Windows Millennium Edition
• Microsoft Windows NT Server 4.0 Accepted Edition
• Microsoft Windows NT Workstation 4.0 Developer Edition
How many times have you installed a LAMP server only to find Apache doesn’t seem to want to run right? Or you install a new module only to see Apache try to download pages as file, instead of displaying them on screen?
There are a hundred and one thousand things that can go wrong with any web server installation. From a fresh installation to an installation that has been running for a long time, you never know when something is going to cause your web server to go astray. When it does happen, it’s always nice to know that, usually, Occam’s Razor applies.
In this tutorial you will find some advice that will help you through some of the more common issues that can pop up with an Apache web server.
Is your server actually running?
Believe it or not, this has happened to plenty of administrators. You take the server down, do some maintenance, and when you go to check out the server you’re getting errors. The first thing you do, naturally, is check out that /etc/apache2/apache.conf file to make sure your syntax is correct. But it’s perfect! What’s up? The first thing you might want to check is to make sure the server is running. But you don’t want to just issue the command to start the server or reload the server. Instead, issue the command:
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 status
Which should return something like:
* apache is running (pid 9751).
If not, start the server with either:
sudo /etc/init.d/apache2 start
or
sudo apache2ctl start
NOTE: If you are using a distribution like Fedora, SuSE, or Mandriva you will need to first su to the root user and issue the above commands WITHOUT using sudo.
It’s not running and it won’t start
Did you just make changes to your Apache configuration file? Are the changes correct? If you’re not sure, you can use the apache2ctl command to check the syntax of your configuration file. This is done with the command:
sudo apache2ctl configtext
The above command should report:
Syntax OK
If you don’t get an OK, you will get information that points to the errors in your configuration file.
Apache wants to download .php files!
This is another common issue. When you add a new tool on your web server (such as Drupal), if your configuration file is set up properly, any .php file might not be displayed. Instead any attempt to view a .php file will instead have your browser trying to download the file. Why is this? Apache must be informed that certain extensions are to be displayed, not downloaded. This is done from within the Apache configuration file. Open up that file (in the Ubuntu server it will be /etc/apache2/apache2.conf) and first look for the following line:
DirectoryIndex index.html
If that file doesn’t include index.php nearly all sites that use php will be rendered useless.
The second line to look for is:
AddHandler application/x-httpd-php .php
If you find this line, and it is commented out, make sure you uncomment it by removing the “#” character. If it is not there add it to the bottom of the configuration file.
And, as always, when you make a change to the configuration file, restart Apache.
Know where to look for problems
Finally, it is crucial that you know where to first turn when the above doesn’t help you out. Any time I have an issue with Apache where Occam’s Razor does not apply, the first place I turn is the log files.
If you look in /var/log/apache2 you will find, at least, the following files:
* access.log: This keeps track of any connection made to your server.
* error.log: This keeps track of any errors that occur with Apache.
* other_vhosts_access.log: This is where virtual hosts will log when the virtual host has not been prescribed its own log file.
Of course, as your site evolves so will your available log files. Regardless of what you find in /var/log/apache2, that is where you should always first turn when you have problems. Even before you google.
Final thoughts
Now you should be able to handle some of the more common issues with the Apache server. And if your problem isn’t common, you also know where to turn to find clues that will lead you down the right path to correction.
Here we provide solutions for problems that you may encounter when using the HD Media Player.
Player SWF doesn’t load on page: You must have Flash Player 10 installed (you will probably have to close and reopen your browser to complete the installation), and you must provide a valid path to the SWF on your web server. If you are loading a SWF file that is NOT hosted on the same server as the page where it is being displayed, you must use a crossdomain.xml file in the root of the website that contains the SWF file (this is part of the Flash Player security model).
XML playlist doesn’t load in player: You must provide a valid path to your XML (using FlashVars, ActionScript, JavaScript, or the Component Inspector), and your XML can not contain errors (check all your media paths and use one of our default XML files to check your syntax). If you are loading a XML file that is NOT hosted on the same server as the page where it is being displayed, you must use a crossdomain.xml file in the root of the website that contains the XML file (this is part of the Flash Player security model).
Bandwidth detection doesn’t work: You must provide a valid path to your bandwidth test location (using a parameter in the XML or Component Inspector). Please refer to our “Automated Bandwidth Detection” tutorial for more information.
Fullscreen doesn’t work or player doesn’t resize correctly when exiting fullscreen: You must have Flash Player 10 installed (you will probably have to close and reopen your browser to complete the installation); you must be testing your SWF in a web page using a web browser (will not work on your desktop); and you must set the “allowfullscreen = true” in your embed code. If you have altered the size and/or location of any objects on the stage, you also have to modify a few lines of action script to account for the new layout. Please refer to our “Fullscreen Setup and Resizing” tutorial for more information.
JavaScript interaction doesn’t work: You must provide valid paths to all of your media files; you must define the “id & name” of your SWF in the embed code; you must test your SWF on a web server using a browser (i.e. will not work locally, swf must be embedded in a webpage, and the SWF can not be inside a form tag); and you must have JavaScript enabled in your browser. Please refer to our “JavaScript Interaction” tutorial for more information.
H264 (mpeg-4) files cannot be seeked before they are completely downloaded: The MOOV atom in your H264 files is located at the end of the file. To fix this problem you should re-encode the file using Adobe Media Encoder or QuickTime Pro. Alternatively, you could try using the QTIndexSwapper, but it may not work in all cases.
MP3 playback is too fast or too slow: Your MP3 contains variable bit rate encoding or unsupported sample frequencies (e.g. 48Khz). To fix this problem you should re-encode the track using constant bit rate encoding and a supported frequency (11, 22, 33, or 44 kHz), which can be done with iTunes.
Video duration/dimensions are wrong or progress bar/scrubbber doesn’t work: Your media file does not include metadata. To fix this problem you can manually define the duration using the “dur” attribute in
Progressive (http) FLV file doesn’t work: You must provide a valid path to your progressive media file. If you are using a relative path it must be relative to the location of the page where it is being used (not the location of the SWF). If you are using a Windows 2003 server (Microsoft IIS Server 6.0), make sure the FLV mime type has been added to the server (link to simple instructions).
Streaming (rtmp) file doesn’t work: You must use a supported server type (FMS 3.x, Wowza, or Red5); you must provide a valid path to your streaming media file (correct syntax based on file type); and you must use the correct ”instance” setting to help the player parse your rtmp path. Please refer to our “Working with a Flash Media Server” tutorial for more information.
the concept of DNS and, perhaps more importantly, how to manage it in an organization. We looked at a number of ways of keeping your thumb on DNS.
The first way we looked at was simply the Monitor tab of your DNS server properties dialog box. The main use of this tab is to perform some queries against your DNS servers. You can perform either recursive or iterative queries against your servers (remember those?)
The next tool we looked at was NSLOOKUP. NSLOOKUP is a command line tool and uses reverse lookup zones (remember those?) to lookup your name servers, hence the name. We discussed the various things you can do with NSLOOKUP, and instead of rehashing them here, check out this link to get more information.
The next tool we looked at was a powerful DNS tool called DNSLint. This tool is available from the Windows Support Tools and is used to do some advanced DNS troubleshooting. Depending in which options we use with the command, we can do various things. For example, running dnslint /d boston.contoso.com will test the boston.contoso.com domain to ensure that it has proper DNS connectivity. Again, TechNet has more information here.
Next up, we looked at the DNSCMD command, which can be used to directly manipulate the DNS database. If, for example, I want to insert a Host (A) record pointing traffic aimed at mailserver.contoso.com to 10.1.5.1 I would type in this from the command prompt:
dnscmd dnsserver.contoso.com /recordadd mailserver A 10.1.5.1
The last thing we discussed was Replication Monitor, which is launched simply by issuing the replmon command from the command prompt. This command allows us to ahem, monitor replication to discover any errors that might be happening.
Windows 7 includes a wealth of features that improve your productivity at work in addition to providing fun activities for you and your family to enjoy using your PC even more. But there might be a time when a problem might occur that you need to solve on your PC, whether its hardware or software related. Windows runs on over 1.2 billion configurations world-wide. That’s a lot of PC’s and its a testament to how well designed and sophisticated the Windows platform is, to make it work on the variety of setups that exist around the world. The Windows Team does its extreme best to make the Windows experience trouble free, but there is always a chance that something will go wrong from time to time. Not to worry though, because Windows 7 in particular introduces a set of easy to use solutions that can help you get out of a mix or suggest a quick fix. Today, I want to take a look at some of these tools in addition to the improvements that this major release of Windows introduces.
Windows Troubleshooter
Windows 7 includes a new trouble shooting utility called Windows Troubleshooting, which diagnoses and resolves common operating system, application and hardware issues by providing built-in troubleshooters for several different types of problems. Whether its power management, performance, programs, networking or printers just to name a few. Some troubleshooters that come with Windows 7 automatically run in the background on a scheduled basis. If they discover a problem they will let you know in the Action Center. Examples of such scheduled maintenance tasks include cleaning up temporary files, detecting hard disk errors, removing broken shortcuts, and ensuring the system time is correct. Lets take a look at utilizing Windows Troubleshooter. In this scenario, I am having some problems accessing a shared folder on another PC. To start the the Troubleshooter, click Start, type: Troubleshooter
As you can see the Troubleshooting Control Panel list a collection of available Task that Windows users can use to diagnose common problems that you might be experiencing. Windows 7 includes a collection of 20 common Troubleshooting Task. The Action Center will notify you of new and updated troubleshooters when they’re made available online, as provided by Microsoft or your computer vendor.
My specific problem as indicated by the error in the Network explorer I am having a problem ‘accessing shared files and folders on other computers. Its exactly what I am looking for! Lets click it and see what its all about. As you can see below, a wizard is started, specifically designed to resolve problems related to Shared folders.
The wizard runs a quick diagnostics test then ask for some form of input if necessary, this will vary by Troubleshooter. In this case I am being asked for the Network path (location) that I need access to. Going back to Network Explorer, clicking in the Address Bar, the name reveals it is located within \HOME-DELLX86 while the name of the folder I need access to is ‘SharedDocs’ so, the path I should type in the Troubleshooter wizard is ‘\HOME-DELLX86\SharedDocs’, lets go ahead and do that.
Troubleshooting success!
After entering the necessary information, the wizard will run a series of test, attempting to correct the problem. The wizard will then ask you to close the Troubleshooter and check if the problem is corrected. If you are interested, you can monitor a history of all your troubleshooting activities. Users must note that, Windows Troubleshooting is not or never will be a complete answer, but it compliments the array of options available to Windows users when trying to solve a problem.
Compatibility
Compatibility is always a sensitive issue when it comes to a new version of Windows. Microsoft takes it very seriously and considers it a hallmark of the Windows platform, making it easy for users to transition to a new release with little or no hiccups. With the release of Windows XP, Microsoft introduced Compatibility Mode, which let older applications run on the OS emulating supported versions of Windows with the ability to save settings so that your applications will start in the correct mode every time. Compatibility Mode worked in some cases and others it did not.
Windows Vista’s compatibility story was a tough one, simply because of the fundamental changes that were made to enhance the system’s security foundations. In Windows 7, the Compatibility process is handled through a number of avenues, which include the Windows Upgrade Advisor and Application Compatibility Toolkit (ACT) to help customers assess application compatibility. Microsoft is tackling compatibility through shims, which avoids some of the problems that programs encounter when trying to function on a new version of Windows. Windows Vista affected compatibility through new improvements to its account privileges called Standard User Mode.
Because of the limitations of Standard User, applications that were designed to run with only Administrative privileges could not function properly under Vista, there is both a good and bad here, the good being malware could not easily infiltrate a system, but at the same time, the user would not be able to use a desired application effectively. With Shims, an application is prepared to run with Administrative privileges by making the application believe it has full rights while still in Standard Mode. Windows 7 provides a total of 6,999 shims for applications with more expected every patch Tuesday. Companies can create their own shims using the Windows Application Compatibility Toolkit recently updated to version 5.5, this helps with diagnosis of compatibility problems and the ability to apply the proper shims for troublesome programs. ACT also offers a shim that helps a custom application locate system files written in an unexpected directory as a result of different versions of the operating system.
One of the common ways to work around application compatibility problems in Windows 7, is to use the interactive right-click method and click the Run as administrator contextual menu option. To occasionally run an application with a full administrator access token, use the following procedure.
To perform this procedure, you must be logged on as a local administrator or provide the credentials of a member of the local Administrators group.
1. Locate the program icon or a shortcut in Windows Explorer
2. Right-click the program icon or shortcut, and then click Run as administrator.
3. When the UAC message is displayed, do one of the follow:
* If you are logged on as a standard user, or if UAC is configured to always require credentials, enter the appropriate administrative credentials, and then click OK.
* If you are logged on as an administrator and UAC is not configured to always require credentials, click Yes to start the application.
If the above does not provide a solution, you can utilize the Program Compatibility troubleshooter. If an older program does not run correctly, you can use it to simulate the behavior of earlier versions of Windows. Program Compatibility troubleshooter runs a quick diagnostic check which searches for a list of programs that you might be experiencing problems with. If you don’t see the program, you can click ‘Not Listed’, click next and browse your hard disk for the program. If your program is listed, select it and click Next. Program Compatibility will then suggest recommended options. Personally, I prefer choosing ‘compatibility settings based on problems you notice’. As I noted earlier, most application issues are often related to compatibility with the OS.
Windows will then ask you to check off any of the behaviors you are noticing when attempting to use the program. All may not apply and most often, choosing an earlier version of Windows that the program worked in can resolve the problem. For my scenario, I will select ‘The program worked in earlier versions of Windows but won’t install or run now’. Program Compatibility will then list versions of Windows that the program worked in. Select one and the Program Compatibility Troubleshooter will reconfigure the application to run the appropriate settings.
Preparing an incompatible application to work in Windows 7
Problem Steps Recorder
Problem Steps Recorder is used to capture application compatibility issues for evaluation by technical experts. It does this by automatically capturing the steps you take on a computer, including a text description of where you clicked and picture of the screen during each click. Once you capture these steps, you can save them to a file that can used by a support technician or an expert to resolve the problem you might be experiencing.
System Restore
Last year I did a CISCO IT Essentials course which prepared me for the CompTIA A+ exam. One of the things I discovered during my learning was how important System Restore is in the troubleshooting process for Technical Support staff. Microsoft first introduced System Restore with the release of Windows Millennium Edition in 2000. Since then the Windows Team has included it with new versions of Windows while improving the reliability of this essential utility. With Windows 7, there are some welcome improvements I want to take a quick look at.
System Restore provides an opportunity for users to restore their PC to an earlier time in case of a problem. Windows saves snapshots of the system in its current condition. By taking a snapshot before installing a program, you can correct the problem by rolling back your computer to a point in time when it was working well. The great thing about System Restore has always been the ability restore with confidence knowing that your personal files will not be altered or destroyed during the process. System Restore affects Windows system files, programs, and registry settings. It can also make changes to scripts, batch files, and other types of executables created under any user account on your PC.
In Windows 7, System Restore is more reliable, predictable, and effective. You’ll see a list of programs that will be removed or added, providing you with more information on which restore point to choose. System restore points are also available in your backups, giving you a larger list of restore points to choose from—and likely over a longer period of time. When combined with other features such as Previous Versions which are copies of files and folders that Windows automatically saves as part of a restore point Windows users can feel secure knowing their information is always protected by the OS.
Recently I took a look at the two other important troubleshooting features in Windows 7, Recovery Options, Backup and Remote Assistance.
Windows 7 includes advanced recovery options that can guide you through the ‘reinstallation of Windows’ and restoration of personal files and settings. This will require that you have an available Windows 7 installation disc or Recovery Image, which will assist with the reinstallation. You will have to restore your files from a backup, programs must also be reinstalled. Most OEM’s (Original Equipment Manufacturers) such as HP, Lenovo and Dell install a hard drive partition customized with additional tools such as a separate system recovery tool for restoring the computer back to its original state. Advanced Recovery also includes the option to backup files before starting this procedure. You can find the Advanced Recovery option in Control Panel > Action Center > Recovery > Advanced recovery methods. Read the entire article here
Windows 7 backup and restore features are designed to make protecting your data and system easier. The combined file and system backup wizard delivers a simplified configuration experience, and the folder selectivity functionality for file backup provides users greater control over their backup content. Managing backup is easier with the new space management user interface and integration with Action Center. Recovering your system is made easier with simplified interface and better guidance for choosing a recovery method. Read the entire article here
Remote Assistance in Windows 7 introduces a new feature called ‘Easy Connect’ which simplifies the process of connecting to another PC remotely with only a password, no file needed. When a connection is established between both computers, contact files are exchanged which creates a trust relationship. This further simplifies future connections that are made without the need for a password. Read the entire article here
Conclusion
Windows 7 makes troubleshooting a worry free process that emphasizes strong confidence when using your PC, protecting your precious memories and critical data. For beginner’s and experts, the operating system covers a wide range of problem solving capabilities that can assist you in the event of a problem. If you ever encounter an issue, just know that Windows 7 got your back! :)
Internet Explorer 7 (IE7) is light years ahead of its predecessors, but by no means does that proclamation mean that the browser is perfect. You are still going to encounter issues with IE from time to time.
Here are some of the concise guides that deliver some troubleshooting steps that will clear up the majority of issues we encountered with IE7.
Issues with Internet Explorer 7.0 with solutions
Problem: Crashes or hangs
If IE crashes, the most likely problem is that there's a buggy add-on (Toolbar or Browser Helper Object). In order to verify and isolate the buggy add-on, follow these steps:
1. Start IE in No Add-ons mode, either by right-clicking the Desktop icon, or clicking START - RUN and typing: iexplore.exe -extoff
2. Determine if IE fails.
3. If not, use Tools - Manage Add-ons to disable all browser extensions and toolbars.
4. Restart IE and re-enable browser extensions one-by-one.
5. Once you've found a broken extension, contact the manufacturer and ask for an update.
(Reference: http://support.microsoft.com/?id=928426)
If IE still crashes often, even when browser add-ons are disabled:
• Please ensure that you are running the very latest version of your anti-virus, anti-malware, and/or firewall programs.
• Please ensure that the drivers for your graphics card are up to date.
• If you have Google Desktop installed, please ensure that you update to the latest version of Google Desktop.
• If you have 7-Zip or other Windows Explorer extensions installed, please ensure that you update to the latest.
Problem: Cannot connect to Internet using IE after updates installed
If you see the "Page Cannot be Displayed" error after installing Internet Explorer updates from Windows Updates, it's possible that you have a 3rd party firewall installed that is blocking access because the IE files have been updated. Please see http://support.microsoft.com/kb/942818/en-us for more information.
Problem: IE always starts in "No Add-ons" mode
The problem is that you're launching Internet Explorer using a shortcut icon that has the "-extoff" command line parameter. That parameter causes IE to start without add-ons. Thus, every time you use that shortcut icon, IE will start in No Add-ons Mode.
1. How do you normally start Internet Explorer? Right-click whatever icon you're using to start IE, choose "Properties" and remove the -extoff part of the shortcut.
2. If you click the green START button, click Run, type iexplore.exe in the RUN box, then hit the ENTER key, IE will start with Addons enabled.
Problem: IE opens small windows
IE opens new windows at the size of the last closed window. If you find that IE is opening small windows, do this:
• Close all IE windows.
• Open one new IE window.
• Adjust that window to the size you prefer. Do this by dragging the window borders. Do not use the maximize button:
• Close the IE window.
• New IE windows will open at the size you chose.
Problem: ClearType Text appears fuzzy
IE7 turns on a text-smoothing technology called "ClearType" by default. ClearType is scientifically proven to make text easier to read, particularly on LCD flat panel monitors.
If ClearType looks fuzzy on your monitor, you might want to try the ClearType tuning wizard, which can help you adjust the display of ClearType.
If you still don't like the appearance of ClearType, you can turn it off by unchecking the checkbox: Tools - Internet Options - Advanced - Multimedia - Always use ClearType for HTML.
Problem: IE Startup takes a long time (>3 seconds)
1. IE may start very slowly if you have a huge number of sites listed in your Restricted or Trusted sites zone. Some tools, like "SpyBot Search & Destroy" will place thousands of sites in these zones if you use their "immunize" feature.
2. Follow the "Crashing on startup" steps above to see if starting in No Add-ons mode starts much faster
3. If you're not using a proxy, uncheck IE's "Automatically detect settings" option on the Tools - Internet Options - Connections - LAN Settings dialog.
Problem: Slow Page rendering
1. Increase the connection limit. This tweak allows IE to make up to 16 connections per server.
2. Ensure that both "HTTP1.1" checkboxes in Tools - Internet Options - Advanced are checked.
Problem: IE7 Setup fails to install Internet Explorer
See http://support.microsoft.com/kb/917925
Problem: My address bar won't turn green?
IE7 includes a cool new feature that turns the address bar green when a secure site presents an Extended Validation certificate:
If you're having trouble with this feature, on a site you know has an EV certificate:
1. Ensure that you either have the Phishing Filter set to "Automatic" mode or Tools > Internet Options > Advanced > Security > Check for Server Certificate revocation checked.
2. If that doesn't work, install this: Windows Root Certificate Update and restart.
Problem: After installing, IE7 starts then vanishes
It's possible that one of IE's DLLs isn't installed correctly
1. Click START - RUN and type cmd
2. In the command prompt, type cd\
3. In the command prompt, type cd Program Files
4. In the command prompt, type cd Internet Explorer
5. In the command prompt, type regsvr32 IEPROXY.DLL
(Reference: http://support.microsoft.com/?id=928427)
Problem: Error message about PSAPI.DLL
If you install IE7 and the following error message begins to show:
The procedure entry point GetProcessImageFileNameW could not be located in the dynamic link library PSAPI.DLL
1. Search your hard disk for PSAPI.dll.
2. Any copies of this DLL that are found outside of the Windows or Windows\System32 folder should be renamed to PSAPI.bak.
Problem: IE always goes to http://runonce.msn.com/runonce2.aspx instead of my homepage
If IE7 always goes to the RunOnce page on startup, even after you've tried to save the first run settings, it's possible that the mechanism that IE is using to save the settings does not work for some reason.
You can prevent IE from going to the RunOnce page and cause it to go directly to your homepage by running this script.
For more info, check out this Knowledge Base article.]
Problem: IE always goes to http://www.microsoft.com/windows/downloads/ie/getitnow.mspx instead of my homepage
If Internet Explorer always goes to this page on startup, it's likely that you have an anti-spyware package (like "SpyBot") that prevented IE from correctly modifying your registry.
Try running this script. Note: you may need to disable your anti-spyware tool temporarily for the script to work.
Problem: On startup, IE always shows an error message about the AOL toolbar
If you see the following error message every time IE starts:
"Cannot find 'file:///C:/Program%20Files/AOL%20Toolbar/welcome.html'. Make sure the path or Internet address is correct."
..then you've hit a bug in the AOL Toolbar.
Try running this script. Note: you may need to disable your anti-spyware tool temporarily for the script to work.
Problem: I installed a "branded" version of IE7, but I'd prefer a "plain" copy without toolbars and customizations.
An article on this topic can be found here: How to remove branding in Internet Explorer 7.
Problem: Malware / Adware
If Internet Explorer is behaving strangely (crashing, visiting unwanted sites, etc), it's possible that there is malicious software installed on your computer.
As a first step, you should allow your antivirus software to scan and attempt to repair your computer. Additionally, you may want to try the following Microsoft tools:
• Windows Defender
• Windows Live OneCare
• Windows Live Safety Center
• Malicious Software Removal Tool
You should also ensure your computer has all the security updates available at Microsoft Update.
Problem: My searches are redirected to unrelated sites and I cannot connect to WindowsUpdate or antivirus websites
If Internet Explorer searches are redirected to unrelated sites or search engines, it's possible that your computer was infected with malware (see the previous tip). However, if your computer is not currently infected with malware, it's possible that at some time in the past, malicious software altered your computer's DNS settings. DNS works like an "internet phonebook" that maps URLs (like "windowsupdate.microsoft.com") to internet protocol addresses (like "207.46.225.221").
To determine if a malicious DNS server is configured:
- Go to Start -> Control Panel ->Network Connections.
- Right click your default connection, usually Local Area Connection or Dial-up Connection, if you are using Dial-up, and left click on Properties.
- Double-click on the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) item
Check to see if you're set to something other than "Obtain DNS servers automatically". If so, contact your ISP to ensure that the address specified is correct, or set the "Obtain DNS servers automatically" checkbox. Then restart your computer.
Problem: After opening many tabs, Windows and IE paint abnormally.
See http://blogs.msdn.com/tonyschr/archive/2005/05/25/desktop-heap-limitations.aspx
Problem: A remote user is having networking problems with Internet Explorer. How can I collect information about his system to help me to troubleshoot?
Have the user run Netcheck and send you the log file.
Problem: Overlong headers result in HTTP/4xx or HTTP/5xx errors, particularly on devices like routers or webcams
Problems of this nature are usually caused by one of the two request headers in yellow being longer than the device expects.
GET / HTTP/1.1
Accept: image/gif, image/jpeg, image/pjpeg, application/x-ms-application, application/vnd.ms-xpsdocument, application/xaml+xml, application/x-ms-xbap, application/vnd.ms-excel, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint, application/msword, application/x-shockwave-flash, application/x-silverlight, application/x-silverlight-2-b2, */*
Accept-Language: en-us
User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 8.0; Windows NT 6.0; WOW64; Trident/4.0; SLCC1; .NET CLR 2.0.50727; .NET CLR 1.1.4322; InfoPath.2; .NET CLR 3.5.30729; .NET CLR 3.0.30618; OfficeLiveConnector.1.3; OfficeLivePatch.1.3; MS-RTC LM 8)
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Connection: Keep-Alive
Host: 192.168.10.1
These headers are dynamically generated out of registry keys. They can usually be trimmed by editing the registry without any important side-effects.
To trim the list in the Accept header, click START > RUN > REGEDIT.EXE. Using RegEdit, navigate to:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\Accepted Documents
..and remove elements from the "Name/Type/Value" list to remove values that aren't strictly required. Elements in red are of lower importance than those in black:
image/gif, image/jpeg, image/pjpeg, application/x-ms-application, application/vnd.ms-xpsdocument, application/xaml+xml, application/x-ms-xbap, application/vnd.ms-excel, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint, application/msword, application/x-shockwave-flash, application/x-silverlight, application/x-silverlight-2-b2, */*
A similar problem can occur with the User-Agent header.
To trim the list in the User-Agent header, click START > RUN > REGEDIT.EXE. Using RegEdit, navigate to:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\5.0\User Agent\Post Platform
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\User Agent\Post Platform
..and remove elements from the "Name/Type/Value" list to remove values that aren't strictly required. Elements in red are of lower importance than those in black:
User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 8.0; Windows NT 6.0; WOW64; Trident/4.0; SLCC1; .NET CLR 2.0.50727; .NET CLR 1.1.4322; InfoPath.2; .NET CLR 3.0.30618; .NET CLR 3.5.30729; OfficeLiveConnector.1.3; OfficeLivePatch.1.3; MS-RTC LM 8)
You see, we should be very thankful that we are born in this modern generation because of the existence of the Internet. With the Internet, every information (whether about dedicated exchange server hosting or any other such as freebsd dedicated server, tomcat hosting, discount dedicated server or even freebsd dedicated server) can be found with ease on the Internet, with great articles like this.
Getting your own dedicated server for your business is a great idea if you are interested in security, being the only business on the server, eliminating potential server problems, and have a budget that includes a substantial monthly fee.
The next thing you need to consider would be if the dedicated server you would be getting will be managed or unmanaged. If you are very knowledgeable, and you have an idea on how you would be managing the server on your own, then you could go for an unmanaged server, but if you do not, it would be recommended to get a managed dedicated server.
If you don't have an IT staff or a server administrator to provide support, you may want to find a person to help you manage your dedicated server. Many hosting companies that offer dedicated server plans also offer "per issue" support, meaning that you'll pay a certain amount, usually an hourly fee, for technical support issues. Some dedicated server plans have optional "support tickets" that you can purchase in advance.
Don't forget that you are only a step away from getting more information about dedicated exchange server hosting or such related information by searching the search engines online. Google.com alone can give you more than enough results when you search for dedicated exchange server hosting.
In a summarized form go for a dedicated exchange server if the website is in a category of most popular, and it is having tons of daily visitors, if work is on B2B basis, if additional security and functionality are required then its time to go for a dedicated server.
A unique IP address is the fifth important advantage. With a dedicated exchange server, you are guaranteed to have a unique IP address. A shared server has one IP address and special header-reading software determines which website traffic is directed to which actual site. This can slow down a server. Upgradeability is the sixth advantage. You are free to upgrade your dedicated exchange server any way you like.
You also benefit from the lack of sharing going on. You don't have to worry about server problems resulting from multiple users. You don't have to worry about server space, since no one else is using the server's resources. You are free to install any information or software that you want. A dedicated exchange server hosting allows you more freedom, as well as the reduction of down time. Lastly, a dedicated server usually loads content faster and provides an overall more prompt user experience for your customers.
Many people looking for information about dedicated exchange server hosting also looked online for hosting and dedicated server, ut2004 dedicated server, and even bf2 dedicated server linux.
Due to the very nature of secure channel establishment, it is often difficult to even approach troubleshooting and debugging SSL related issues.
This brief article intends to illustrate the challenges, approaches and tools available for debugging these difficult scenarios.
SSL Description
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) is a protocol for providing a secure channel of communication between two computers. It makes provisions for data integrity, confidentiality and authentication. Authentication of the server - by the client - provides an assurance of the fact that the traffic has not been diverted to an attacking server. Mutual authentication requires the client to provide credentials to the server over the secure channel.
SSL Handshake Overview
In order to really be able to troubleshoot and debug SSL related issues, we need an understanding of what the protocol actually does on both the client and server sides. This understanding will enable us to quickly categorize the type of problem being encountered and hopefully a category of approaches for tracking down the root cause.
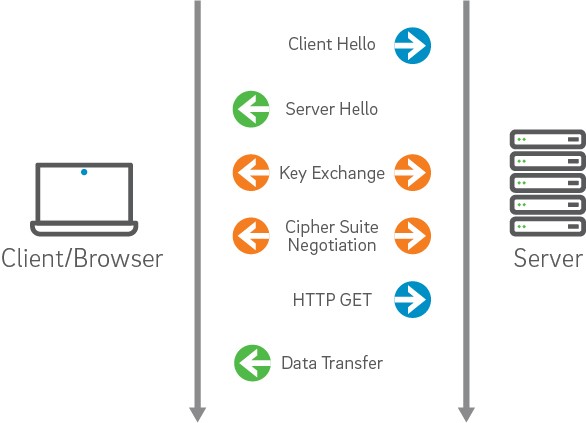
We will touch on issues and troubleshooting approaches in the following categories:
1. Certificate Validation
2. Trust
3. Configuration
So let's briefly describe the protocol with a bit of focus on these three categories.
The client initiates the SSL connection by requesting a channel through the use of a ClientHello handshake message. This message contains the Cipher Suites that are configured to be supported by the client side and are available for the server to choose in creating the most secure channel configuration possible between the two machines. It also contains a random number to be used by the server in the generation of keys - this random number is a result of the configured or default RNG on a given platform.
The server side, in turn, responds with a ServerHello that includes the Cipher Suite selected by the server as the most appropriately secure suite for the channel. If a suitable cipher suite could not be selected from the list of supported suites provided by the client - the request for an SSL connection is denied by the server. It also includes a random number and the certificate that is to be used for authenticating the server to the client. This certificate must be validated by the client in order for it to be trusted as representing the identity asserted by it.
This validation is based on a number of possible factors (driven by configuration):
1.Whether it is expired
2.Whether it has been revoked
3.Whether it was issued by a trusted Certificate Authority
4.Whether the server name within the certificate matches the host name for the current connection
Where Things Can Go Wrong
There are a number of common scenarios that occur as a result of improperly configured environments, clients, servers and certificates that can be categorized into one or more of the afore mentioned categories.
The following are a few descriptions of these scenarios and what the approach to identifying the root cause might be.
Keystores and Truststores
- Categories: Configuration, Trust, Certificate Validation
The client (for mutual authentication) and server each present the other a certificate that represents the identity of the machine its running on. In order for either to present this certificate - it must be available within the appropriate Keystore.
Tip 1: Determine the default certificate for a machine as appropriate for your server and ensure that it exists within the configured Keystore and is available to the process that needs to present it to the corresponding partner process.
Tip 2: Ensure that the issuer of the presented certificate exists within the appropriate Truststore of the recipient process.
Supported Cipher Suites
- Categories: Configuration
As described earlier, the handshake involves the selection of the most secure Cipher Suite by the server from the list of supported suites presented by the client.
If there isn't a common Cipher Suite between the client and server, then there is no way for the two machines to establish a secure channel - as there is no common language that will be understood buy each party that provides the necessary protection offered by SSL.
Tip 3: Ensure that the appropriate Cipher Suites are enabled on the client and server sides in order to establish this common language for secure message exchange.
Tip 4: Utilize SSL debug information to determine which cipher suites has been selected
...
...
Tip 5: Utilize a tool such as SSLDump as necessary to see details of the handshake and application data message exchanges
...
11 1 0.0035 (0.0035) C>S SSLv2 compatible client hello
Version 3.1
cipher suites
TLS_RSA_WITH_RC4_128_MD5
SSL2_CK_RC4
TLS_RSA_WITH_RC4_128_SHA
TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_RC4_128_SHA
TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_RC4_128_SHA
Unknown value 0x4e
Unknown value 0x2f
Unknown value 0x35
Unknown value 0x4b
Unknown value 0x4c
TLS_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA
TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA
TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA
Unknown value 0x50
TLS_RSA_WITH_DES_CBC_SHA
TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_DES_CBC_SHA
TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_DES_CBC_SHA
TLS_ECDH_ECDSA_WITH_DES_CBC_SHA
Unknown value 0x4f
TLS_RSA_EXPORT1024_WITH_RC4_56_SHA
TLS_DHE_DSS_WITH_RC2_56_CBC_SHA
TLS_RSA_EXPORT1024_WITH_DES_CBC_SHA
TLS_DHE_DSS_EXPORT1024_WITH_DES_CBC_SHA
TLS_RSA_EXPORT_WITH_RC4_40_MD5
SSL2_CK_RC4_EXPORT40
TLS_DHE_DSS_EXPORT_WITH_DES40_CBC_SHA
TLS_DHE_RSA_EXPORT_WITH_DES40_CBC_SHA
TLS_RSA_EXPORT_WITH_DES40_CBC_SHA
TLS_DH_anon_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA
TLS_DH_anon_WITH_RC4_128_MD5
TLS_DH_anon_WITH_DES_CBC_SHA
TLS_DH_anon_EXPORT_WITH_RC4_40_MD5
TLS_DH_anon_EXPORT_WITH_DES40_CBC_SHA
TLS_DHE_DSS_EXPORT_WITH_DES40_CBC_SHA
TLS_DHE_RSA_EXPORT_WITH_DES40_CBC_SHA
TLS_RSA_EXPORT_WITH_DES40_CBC_SHA
TLS_DH_anon_EXPORT_WITH_DES40_CBC_SHA
11 2 0.0053 (0.0017) S>C Handshake
ServerHello
Version 3.1
session_id[0]=
cipherSuite TLS_DH_anon_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA
compressionMethod NULL
11 3 0.0053 (0.0000) S>C Handshake
ServerKeyExchange
Short read: 0 bytes available (expecting 2)
11 4 0.0065 (0.0012) S>C Handshake
ServerHelloDone
11 5 0.0976 (0.0910) C>S Handshake
ClientKeyExchange
DiffieHellmanClientPublicValue[128]=
8a 23 78 02 8a a5 fc 03 f4 9b 7c 33 05 22 36 91
85 9d 17 e4 bf bf 0a 3e be 45 25 47 07 e0 9c a2
e5 d6 bf 78 95 f1 84 ca cb cc e4 3e f3 d8 d4 9a
3a 01 71 5c 29 0c 0b f9 69 8d 3e a6 f4 08 f0 36
18 fd a7 b9 3e 30 4e a4 a6 19 d9 d3 64 1c 3c 78
d3 c3 fa 83 07 58 f2 be d2 32 80 c0 32 4e 49 4c
bf 73 1a f2 d8 fd f2 16 c7 31 da 48 58 50 bb 99
3f a4 8c 31 6e 5f ed e8 0d d8 91 cf 8f eb fa d8
11 6 0.0976 (0.0000) C>S ChangeCipherSpec
11 7 0.0976 (0.0000) C>S Handshake
11 8 0.0997 (0.0021) S>C ChangeCipherSpec
11 9 0.1000 (0.0002) S>C Handshake
11 10 0.3580 (0.2580) C>S application_data
11 11 0.3580 (0.0000) C>S application_data
11 12 0.3586 (0.0005) S>C application_data
11 13 2.5039 (2.1453) C>S application_data
11 14 2.5039 (0.0000) C>S application_data
11 15 2.5053 (0.0013) S>C application_data
8 20 31.4483 (3.3621) C>S application_data
8 21 31.4483 (0.0000) C>S application_data
8 22 31.4507 (0.0024) S>C application_data
8 23 31.4508 (0.0000) S>C application_data
8 24 32.0824 (0.6316) C>S application_data
8 25 32.0824 (0.0000) C>S application_data
8 26 32.2550 (0.1726) S>C application_data
8 27 32.2550 (0.0000) S>C application_data
8 28 33.1710 (0.9159) C>S application_data
8 29 33.1710 (0.0000) C>S application_data
8 30 33.1745 (0.0035) S>C application_data
8 31 33.1754 (0.0009) C>S application_data
...
Anonymous Cipher Suite
- Categories: Configuration
The failure of a client or server to reject a certificate that is not trusted may present as potential SSL problem. Recall earlier that I describe the process of selecting the most secure Cipher Suite common between both parties.
In a scenario where one of the parties has only the anonymous Cipher Suite enabled and the other party also has it enabled - even if it is one of many - the anonymous cipher suite will be selected and the connection will not be rejected.
Tip 6: see Tip 5 above - in fact, the example ssldump output above is from troubleshooting just such a scenario
Trusted CA's
- Categories: Trust, Configuration
Unless the issuer of a certificate is found in the Truststore of a client or server involved in the establishment of an SSL connection, the certificate validation will fail.
Tip 7: Determine the Truststore/s in use and whether or not the issuer of the presented certificate exists within the configured Truststore
Tip 8: Utilize keytool in order to dump the contents of the Truststores (or keystores for the presented certificates)
Alias name: ttelesecglobalrootclass3ca
Creation date: Feb 10, 2009
Entry type: trustedCertEntry
Owner: CN=T-TeleSec GlobalRoot Class 3, OU=T-Systems Trust Center, O=T-Systems Enterprise Services GmbH, C=DE
Issuer: CN=T-TeleSec GlobalRoot Class 3, OU=T-Systems Trust Center, O=T-Systems Enterprise Services GmbH, C=DE
Serial number: 1
Valid from: Wed Oct 01 03:29:56 PDT 2008 until: Sat Oct 01 16:59:59 PDT 2033
Certificate fingerprints:
MD5: CA:FB:40:A8:4E:39:92:8A:1D:FE:8E:2F:C4:27:EA:EF
SHA1: 55:A6:72:3E:CB:F2:EC:CD:C3:23:74:70:19:9D:2A:BE:11:E3:81:D1
Signature algorithm name: SHA256withRSA
Version: 3
Extensions:
#1: ObjectId: 2.5.29.15 Criticality=true
KeyUsage [
Key_CertSign
Crl_Sign
]
#2: ObjectId: 2.5.29.19 Criticality=true
BasicConstraints:[
CA:true
PathLen:2147483647
]
#3: ObjectId: 2.5.29.14 Criticality=false
SubjectKeyIdentifier [
KeyIdentifier [
0000: B5 03 F7 76 3B 61 82 6A 12 AA 18 53 EB 03 21 94 ...v;a.j...S..!.
0010: BF FE CE CA ....
]
]
Certificate Expiration
- Categories: Certificate Validation, Configuration
Tip 9: see Tip 8 above - In the example keytool output above you can see the dates for which the particular certificate is valid.
Valid from: Wed Oct 01 03:29:56 PDT 2008 until: Sat Oct 01 16:59:59 PDT 2033
Random Number Generation (RNG) Issue
- Categories: Configuration
Performance issues may be encountered due to low or zero entropy on a server. This entropy results in longer than expected blocking in acquiring the random number seeding from /dev/random. There are a couple potential workarounds.
1.use /dev/urandom - NOTE: this may result in degenerated encryption strength and must be investigated by your system/security administrators
2.patches may be available for your particular Linux flavor or Solaris
Tip 10: Observe through SSL debug output whether or not the handshake is timing out as this is an indicator that perhaps we are blocking on the RNG
Tip 11: Ensure that all related patches have been installed on your machine.
Available Tools and Facts
Like any other specialization, troubleshooting and debugging security - and SSL in particular - presents unique challenges and to address these unique challenges we need to be prepared by having appropriate tools and facts at our disposal.
In order to be productive in this area, we need to know certain things about the environment, management consoles, etc.
Debug output
Each middleware platform provides the ability to configure the server to run with SSL debug logging turned on. This configuration enables the viewer of the logs to see pertinent information regarding the configuration and runtime behavior of the handshaking and application data message exchanges in real time.
Tip 12: Determine what the configuration mechanism is for turning on SSL debug information on your platform. On WebLogic Server the following System Properties are used to configure SSL debug information and can be used on the command line or within start up scripts:
-Dssl.debug=false -Dweblogic.StdoutDebugEnabled=true -Dweblogic.security.SSL.verbose=true
Tip 13: When you have access to starting the server with these System properties do so immediately - the information that it creates will be valuable - if not to you then to someone else that is pulled in to help debug - at which time you will be request to do so anyway and go through the whole thing again.
SSLDump
In cases where we don't have access to the server to restart with SSL debug logging or when we would like to supplement that output with additional information SSLDump is hugely valuable.
ssldump is an SSLv3/TLS network protocol analyzer. It identifies TCP connections on the chosen network interface and attempts to interpret them as SSLv3/TLS traffic. When it identifies SSLv3/TLS traffic, it decodes the records and displays them in a textual form to stdout. If provided with the appropriate keying material, it will also decrypt the connections and display the application data traffic.
Tip 14: Download a copy of ssldump from http://www.rtfm.com/ssldump/. You will need to build it on your platform and you may actually need to resolve a couple compilation errors - but it is well worth it.
Examples:
To listen to traffic on port 443:
ssldump -i eth0 port 443
To listen to traffic to the server target on port 443:
ssldump -i eth0 port 443 and host target
To decrypt traffic to the host target server.pem and the password foobar:
ssldump -i eth0 -Ad -k ~/server.pem -p foobar host target
Generic SSL Client
Once you have ssldump built and running on your machine, you can use any SSL client to target the server that you are trying to troubleshoot. Often a browser will suffice - however you may need to build a client more appropriate for your usecase.
Tip 15: Utilize ssldump, SSL debug logging and your SSL client to observe the messages exchanged and the runtime behavior that manifests as a result of your current configuration.
Platform Specific Knowledge
Become intimately familiar with where the appropriate keystores, truststores, configuration files and management consoles are located.
Tip 16: Maintain a checklist of this information and keep it handy so that you don't have to rediscover it every time you encounter SSL issues.
Books
SSL and TLS: Designing and Building Secure Systems, Addison-Wesley, 2001 ISBN 0-201-61598-3
http://www.rtfm.com/sslbook/
PEER 1 Network Enterprises, Inc today announced a collaboration with InMon to provide precise bandwidth measurement and analysis capability.
PEER 1 will deploy the industry standard sFlow® network monitoring technology and InMon’s Traffic Sentinel, in all of its data centers to provide an industry leading bandwidth billing solution for its Managed Hosting customers.
Bandwidth usage is measured on a per-IP address basis, so PEER 1 is able to ignore traffic occurring inside the data center, and provide precise traffic charges to its customers in a way that is not possible through per-port or physical-layer network traffic monitoring.
For PEER 1 customers, the InMon-powered network traffic monitoring and analysis is accessible in real time through the online customer portal with customizable graphs and downloadable data.
Ted Smith, SVP of Operations at PEER 1 said: “We believe our customers should only pay for the services they use and our collaboration with InMon maximizes our network analysis and measurement capability allowing us to accurately pass on lowest cost bandwidth charges to customers. Our IP-based or layer three approach not only increases transparency and billing accuracy, it also enables our customers to accurately re-charge bandwidth usage to their own customers.”
”The unique scalability of InMon’s sFlow solution makes it the ideal choice for monitoring the fastest of data center networks,” said Peter Phaal, president of InMon Corp. “In the expert hands of the PEER 1 engineers, the detailed traffic database in the Sentinel product can be applied to a wide range of applications, from accounting and capacity planning to troubleshooting and security.”
PEER 1 Network Enterprises, Inc today announced a collaboration with InMon to provide precise bandwidth measurement and analysis capability.
PEER 1 will deploy the industry standard sFlow® network monitoring technology and InMon’s Traffic Sentinel, in all of its data centers to provide an industry leading bandwidth billing solution for its Managed Hosting customers.
Bandwidth usage is measured on a per-IP address basis, so PEER 1 is able to ignore traffic occurring inside the data center, and provide precise traffic charges to its customers in a way that is not possible through per-port or physical-layer network traffic monitoring.
For PEER 1 customers, the InMon-powered network traffic monitoring and analysis is accessible in real time through the online customer portal with customizable graphs and downloadable data.
Ted Smith, SVP of Operations at PEER 1 said: “We believe our customers should only pay for the services they use and our collaboration with InMon maximizes our network analysis and measurement capability allowing us to accurately pass on lowest cost bandwidth charges to customers. Our IP-based or layer three approach not only increases transparency and billing accuracy, it also enables our customers to accurately re-charge bandwidth usage to their own customers.”
”The unique scalability of InMon’s sFlow solution makes it the ideal choice for monitoring the fastest of data center networks,” said Peter Phaal, president of InMon Corp. “In the expert hands of the PEER 1 engineers, the detailed traffic database in the Sentinel product can be applied to a wide range of applications, from accounting and capacity planning to troubleshooting and security.”
Physical infrastructures have become the foundation of business’ networks, facilitating communication between the various physical and logical systems in a converged infrastructure and delivering reliable connectivity, security, power, and automation. Increasingly, businesses are deploying the latest converged networking solutions to drive operational efficiency and eco-sustainability. A key trend is to converge physical infrastructure systems on a single IP network to simplify deployment and configuration, centralize management, and help reduce physical footprint and power requirements.
But, while a unified physical infrastructure provides significant cost savings – both short and long term – ultimately, the success of any operation is dependent upon the availability of its network so that users have access to the resources they need to conduct business effectively and efficiently. As such, network uptime and the ability to meet network service level agreements (SLAs) are a critical driver of business success. If you consider network availability as a product, it’s easy to understand that downtime can be as detrimental to business success as poor customer service.
The ability to ensure network uptime requires management solutions designed for today’s complex network infrastructures, including the automated monitoring, diagnosis, and configuration of network assets, to increase efficiency in problem isolation and resolution.
Panduit’s Physical Infrastructure Manager (PIM) solution, with its PanView iQ (PViQ) hardware components are designed specifically to address the complex physical infrastructures that support the access requirements of today’s demanding workforces.
Specifically, the PIM solution adds intelligent management software to the converged data center network, enabling the automation of many tasks, increasing efficiency and reducing risk inherent in manual processes. The real-time visibility enabled by the PIM solution allows network assets to be properly tracked, work order processing and documentation to be automated, management functions to be performed remotely, and, perhaps most importantly for network availability, it is designed to identify connectivity issues and unauthorized access to network resources, which can otherwise result in access failures, inhibiting access to network resources.
When connectivity issues are detected, the solution is designed to quickly restore any failed connections, including assessment of configuration changes required to reinitiate or enhance connectivity. By automating the identification and resolution of connectivity faults, costs associated with time-consuming manual troubleshooting are significantly reduced, and IT staff can focus on other tasks to further business objectives.
In addition, with the entire physical infrastructure connected by a single network, the system is also able immediately identify unauthorized access to the network, whether internal or external. This aids in reducing network resource hijacking, increasing network availability and uptime.
In addition to automated troubleshooting and management functions, Panduit’s solution also provides an easy-to-use interface for manual troubleshooting when required for more effective resolution or preventative measures when strain on certain elements is anticipated.
To further support IT staff in maintaining the network infrastructure and identify recurring points of failure within the network, the PIM solution provides automated reporting and documentation, which can then be used to provide a detailed or high-level overview of network performance, access logs, points of failure, and resolution.
Combined with a UPI-based design, the PIM solution helps IT managers ensure their network resources are being effectively utilized, but also provides the visibility to provide timely alerts when connectivity failures occur – and even provide information required to prevent network failure in the first place.
With the dependence on network connectivity for access to data center resources, this ability is as critical as the physical infrastructure itself. Without proper management capabilities and insight into asset utilization, the infrastructure design can only live up to a portion of its potential in terms of increasing availability and efficiency.
Panduit’s PIM solution supports its broader vision of a unified physical infrastructure by delivering the management capabilities required to ensure the resource optimization enabled by converged infrastructures is fully realized.
Things sure can get spooky in the Troubleshooting section of the new Version 4 Blueprint! Cisco can present a pretty vague issue; give you a very lame diagram; and then really press you for time to solve the Trouble Ticket. In this blog post, I will walk you through this graveyard and attempt to provide some ideas on an efficient and effective approach. For much more detail and practice, our premier products for this exam section are the Volume 4 workbook (currently being edited and improved upon), and the brand new 5-Day Troubleshooting Bootcamp.
Are you ready to find prefixes that go bump in the night? Here is the sample Trouble Ticket we will attack, and the appropriate portion of the Cisco diagram. You will want to have some scratch paper handy (just like in the actual exam). Diagramming can prove to be more important here then in any exam section. You should practice a diagram now based on the show output that follows.

Trouble Ticket 1
Vampires located in VLAN 666 (behind Amityville) are unable to access any resources located behind Transylvania. Correct this issue without static routing, additional routing protocols, or redistribution of any kind.
The first order of business is to “expand” upon their diagram and determine what protocols are in use and where. A quick show ip protocols on each of the devices in the transit path should do the trick.
Transylvania#show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is "eigrp 100"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Default networks flagged in outgoing updates
Default networks accepted from incoming updates
EIGRP metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0
EIGRP maximum hopcount 100
EIGRP maximum metric variance 1
Redistributing: eigrp 100
EIGRP NSF-aware route hold timer is 240s
Automatic network summarization is not in effect
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
53.234.10.23/32
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
Distance: internal 90 external 170
Routing Protocol is "bgp 65001"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
IGP synchronization is disabled
Automatic route summarization is disabled
Unicast Aggregate Generation:
10.10.0.0/16 summary-only
Neighbor(s):
Address FiltIn FiltOut DistIn DistOut Weight RouteMap
53.234.10.44
Maximum path: 1
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
Distance: external 20 internal 200 local 200
HalloweenTown#show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is "eigrp 100"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Default networks flagged in outgoing updates
Default networks accepted from incoming updates
EIGRP metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0
EIGRP maximum hopcount 100
EIGRP maximum metric variance 1
Redistributing: eigrp 100
EIGRP NSF-aware route hold timer is 240s
Automatic network summarization is not in effect
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
53.234.10.44/32
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
Distance: internal 90 external 170
Routing Protocol is "bgp 65001"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
IGP synchronization is disabled
Automatic route summarization is disabled
Neighbor(s):
Address FiltIn FiltOut DistIn DistOut Weight RouteMap
23.10.24.190
53.234.10.23
Maximum path: 1
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
Distance: external 20 internal 200 local 200
Salem#show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is "ospf 1"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Router ID 66.150.201.12
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
Routing on Interfaces Configured Explicitly (Area 0):
FastEthernet0/0
Reference bandwidth unit is 100 mbps
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
102.34.102.12 110 00:30:55
Distance: (default is 110)
Routing Protocol is "bgp 65000"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
IGP synchronization is disabled
Automatic route summarization is disabled
Neighbor(s):
Address FiltIn FiltOut DistIn DistOut Weight RouteMap
23.10.24.200
Maximum path: 1
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
Distance: external 20 internal 200 local 200
CrystalLake#show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is "ospf 1"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Router ID 102.34.102.1
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
Routing on Interfaces Configured Explicitly (Area 0):
FastEthernet0/1
FastEthernet0/0
Reference bandwidth unit is 100 mbps
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
Distance: (default is 110)
Routing Protocol is "bgp 65000"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
IGP synchronization is disabled
Automatic route summarization is disabled
Neighbor(s):
Address FiltIn FiltOut DistIn DistOut Weight RouteMap
66.150.201.12
Address FiltIn FiltOut DistIn DistOut Weight RouteMap
102.34.102.12
Maximum path: 1
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
Distance: external 20 internal 200 local 200
Amityville#show ip protocols
Routing Protocol is "ospf 1"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Router ID 102.34.102.12
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
Routing on Interfaces Configured Explicitly (Area 0):
FastEthernet0/0
Reference bandwidth unit is 100 mbps
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
102.34.102.1 110 00:33:23
Distance: (default is 110)
Routing Protocol is "bgp 65000"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
IGP synchronization is disabled
Automatic route summarization is disabled
Neighbor(s):
Address FiltIn FiltOut DistIn DistOut Weight RouteMap
102.34.102.1
Maximum path: 1
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
Distance: external 20 internal 200 local 200
As I parse the results, I create a more detailed diagram to provide a better picture of what is going on. Looking at the diagram, I immediately contemplate some design issues that could come into play. The iBGP split-horizon rule, next-hop reachability, and synchronization all could come into play here given the protocol configuration.
I decide to start as close the destination as possible and examine the relevant configurations.
Transylvania#show run | section bgp
router bgp 65001
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 10.0.0.0
aggregate-address 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 summary-only
neighbor 53.234.10.44 remote-as 65001
no auto-summary
It appears the intent is to advertise prefixes (the Loopback interfaces) beyond Transylvania using BGP prefix aggregation. Let me ensure that configuration is done correctly.
Sure enough, here is our first BGP configuration issue. We need to advertise a component prefix of the aggregate. The little gremlin that attempted this configuration tried to accomplish this with the network statement, but they got it wrong. Subnetting is being done here of the 10.x.x.x space, so you need to reconfigure the network statement as follows:
Transylvania#show ip int brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 53.234.10.23 YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Loopback1 10.10.10.1 YES manual up up
Loopback2 10.10.11.1 YES manual up up
Loopback3 10.10.12.1 YES manual up up
Transylvania#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Transylvania(config)#router bgp 65001
Transylvania(config-router)#network 10.10.10.0 mask 255.255.255.0
After making this change, I check Salem to see if it is receiving the aggregate from Transylvania and we have reachability:
Salem#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 2, local router ID is 66.150.201.12
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.10.0.0/16 23.10.24.200 0 65001 i
Salem#show ip route bgp
10.0.0.0/16 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 10.10.0.0 [20/0] via 23.10.24.200, 00:06:26
Salem#ping 10.10.10.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.10.10.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 28/33/40 ms
We are on our way to solving this Trouble Ticket…we hope you will follow this blog and continue this (and more) troubleshooting scenarios!
When your hard drive fails you have all the important information like those financial documents and photos that you just cannot replace are lost. You must have options for hard disk drive data recovery. You must store that information somewhere. Generally, on your server hard disk, so it will be placed on your hard drive permanently.
Losing your information forever is the hardest thing to cope with. Microsoft Windows operating system has some basic features to help you maintain your data structures on your disk. You can schedule an automatic de-fragmentation of your hard drives in a month. You can also set this feature to run on RAID configurations which will help with the parity in stripe configuration.
You should place your data on DVDs or CDs for safekeeping. There are other options such as eternal drives in which you can store your data. You can keep printed copies in your file cabinet. If you have a USB drive you can just put that in your pocket.

Now you can try using software application programs for hard disk drive data recovery that are specially designed to protect and retrieve your data. They make many types of software applications and data recovery programs to fit your needs. They cover a wide range of operating systems that are in today's market. You can check Best Buy or even eBay with the latest in data recovery software programs. You can also do a search on Google and find many data recovery companies on the Internet.
Protecting your data from unforeseeable data disasters that you may encounter is important for you. An important aspect of IT professionals’ life, they have to be very protective when it comes to data recovery. If you need help there are data recovery experts everywhere that can assist you in retrieving hard disk drive data recovery.


